Corrosion Around Dental Implants
George, a dentist, asks:
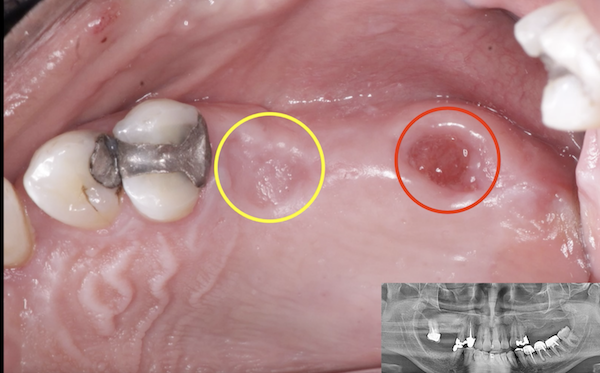
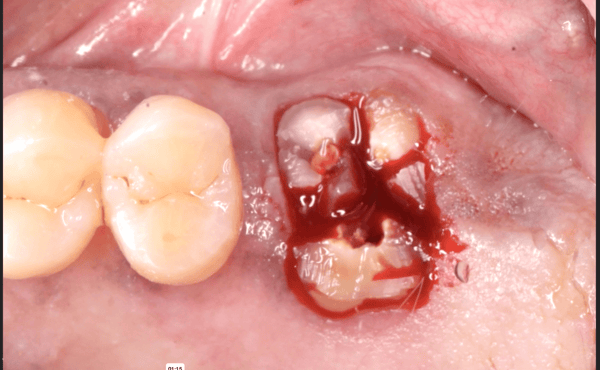
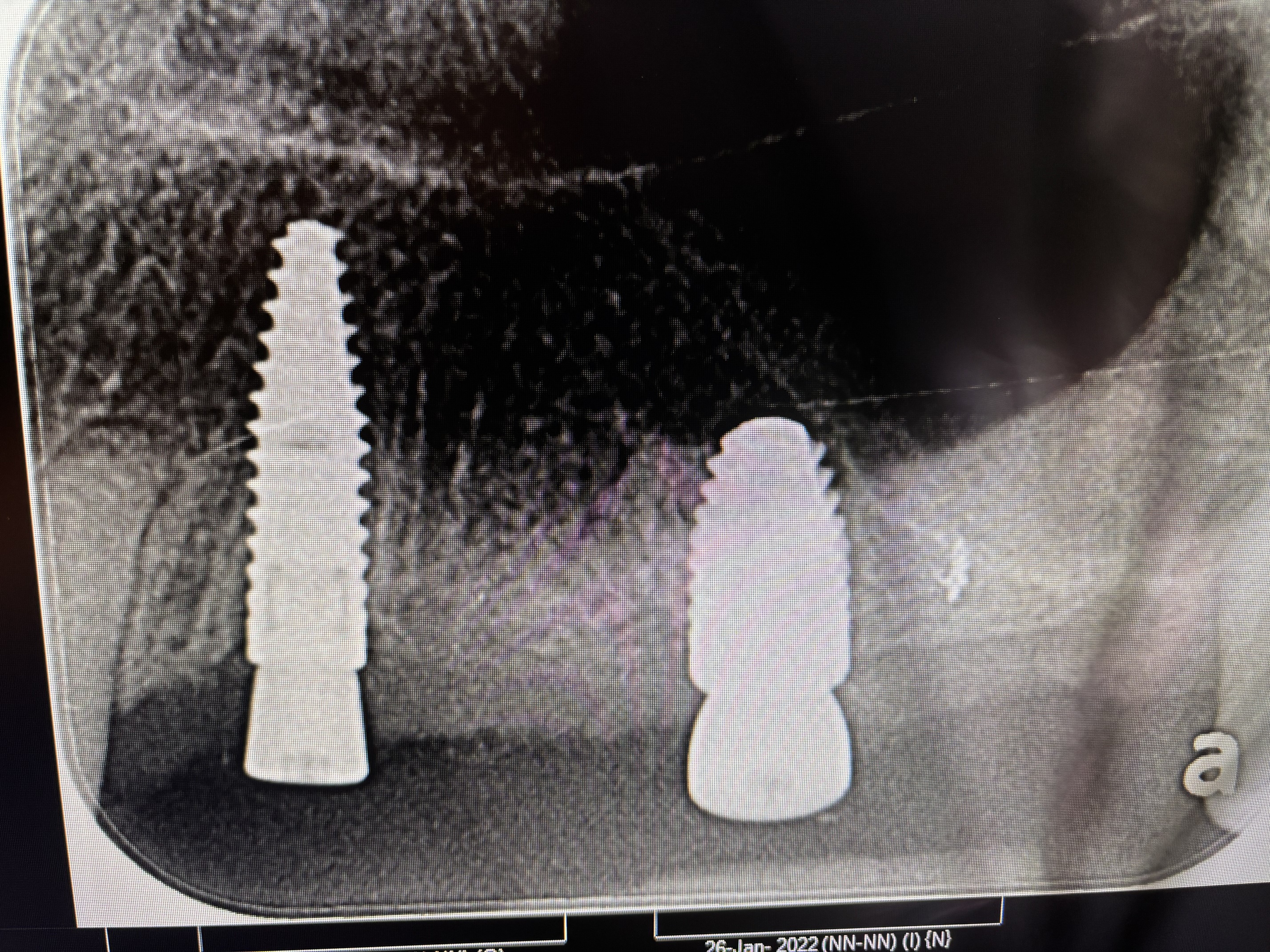
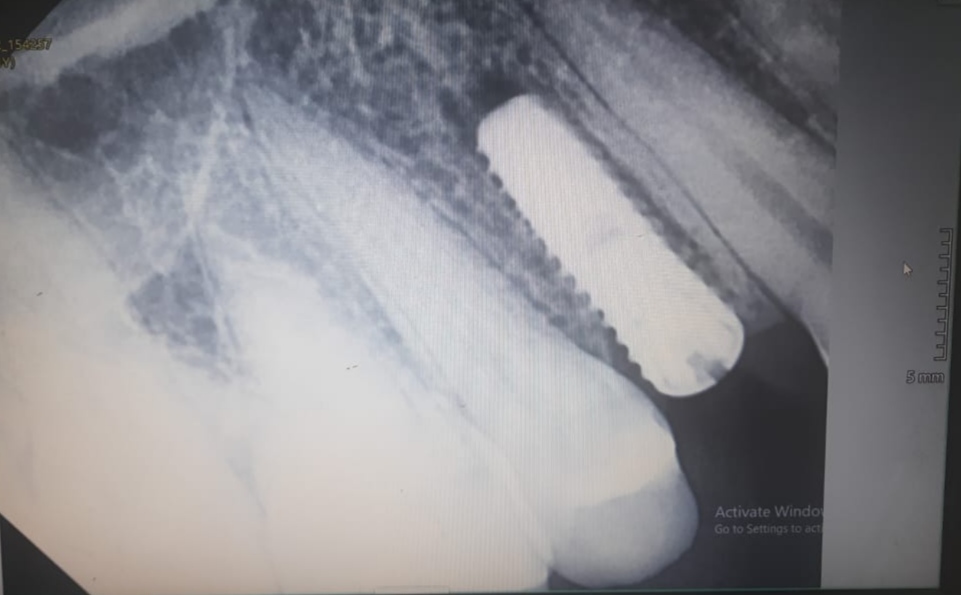
I would like to discuss the problem of corrosion around titanium dental implants. There is a long article recently written that discusses corrosion and how it forms around titanium dental implants.
The article states:
The corrosion of dental biomaterials is a pertinent clinical issue. In spite of the recent innovative metallurgical and technological advances and remarkable progress in the design and development of surgical and dental materials, failures do occur. The clinical significance of the dental implant corrosion is highlighted and the most common form of corrosion i.e. galvanic corrosion is emphasized both in vitro and in vivo conditions.
Source: Adya N, et. al. Corrosion in titanium dental implants: a literature review.
The Journal of the Indian Prosthodontic Society 2005;5:126-131.
Have any other dentists here seen evidence of this corrosion in the titanium implants? If so, is anybody aware of any remedy to fix the problem? Thanks for any insights.