Sponsored Case: Sinus Lift with Synoss Putty and MatrixDerm
Case presentation by: Cory Wanatick, DMD, PA
Diplomate of the American Board of Periodontology, Member of the Academy of Osseointegration, Member of the International Congress of Oral Implantology, American Dental Association, Director of Win Win Study Club
Case Photos
(Case Summary is below. Click on any image for an enlarged view)
![]Wanatick-case-1](https://osseonews.nyc3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Wanatick-case-1-e1383077841657.jpg)
![]Wanatick-case-2](https://osseonews.nyc3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Wanatick-case-2-e1383592748813.jpg)
![]Wanatick-case-3](https://osseonews.nyc3.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Wanatick-case-3-e1383592769992.jpg)
Patient History
A healthy 46-year old female was referred for replacement of teeth #12, 13, 14, and 15 with dental implants because she could not tolerate her maxillary removable partial denture any longer due to discomfort.
Case Summary
Pre-Operative Background
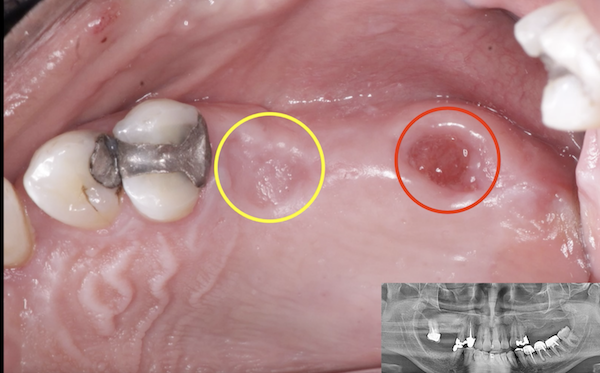
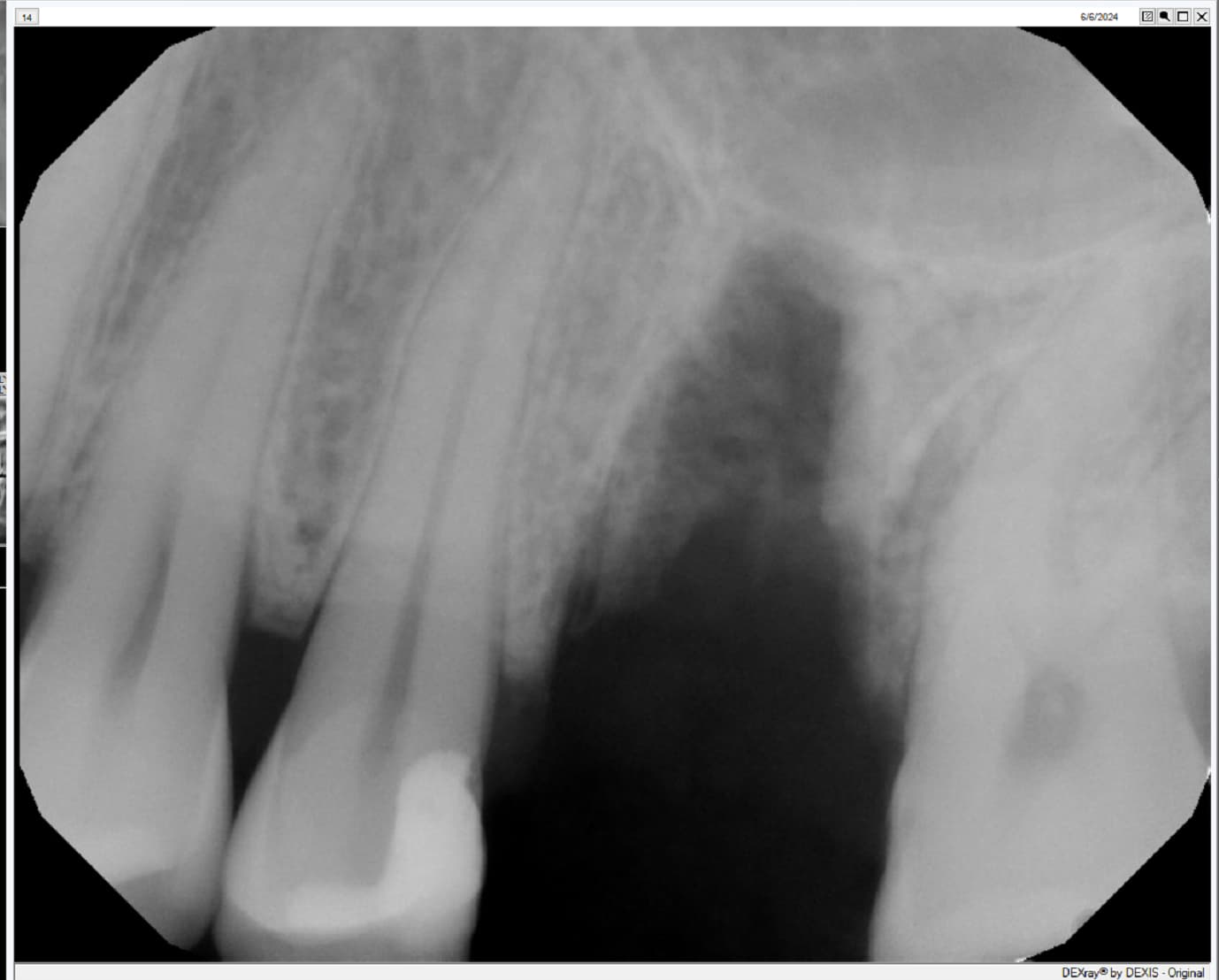
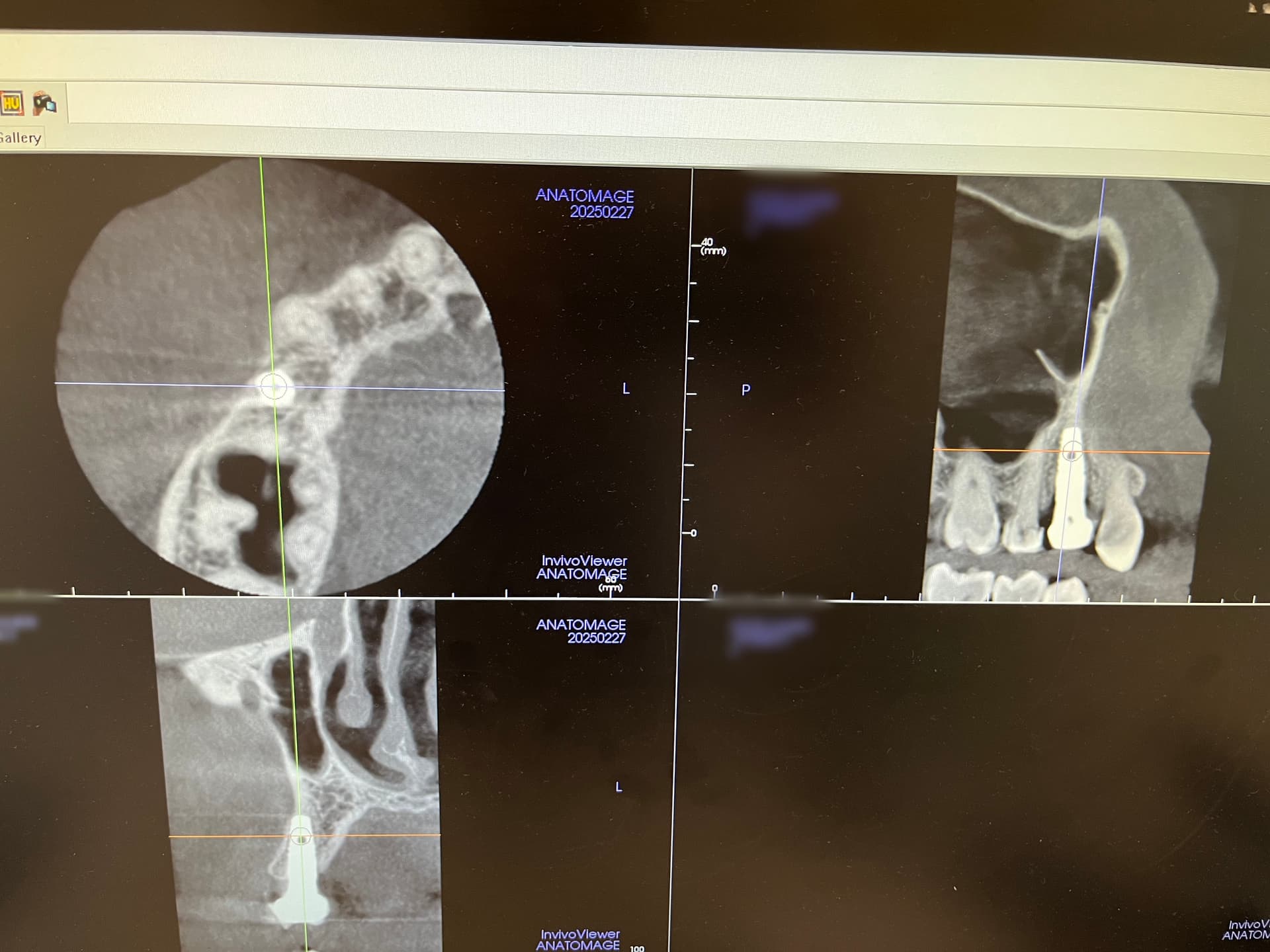
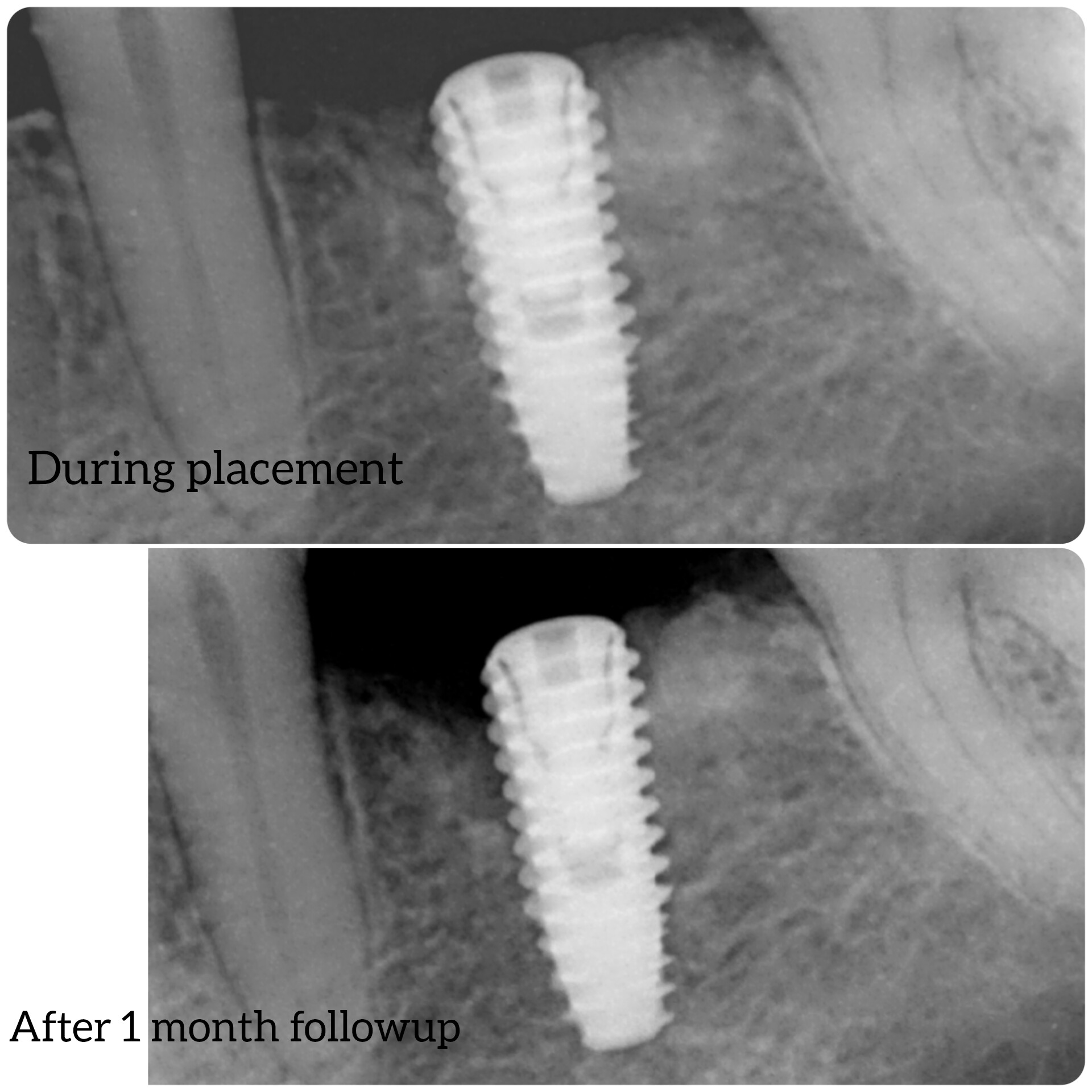
Pre-operative clinical radiographic exam revealed adequate alveolar bone height in the #12 and #13 sites, however, the bone height was inadequate in the #14 and #15 sites due to the pneumatized sinus (Fig 1). The treatment plan would be for placement of 2 dental implants in #12 and #13 sites with simultaneous sinus augmentation in the #14 and #15 sites for delayed implant placement.
Surgical Procedure #1
Following a preoperative rinse of 0.12% Chlorhexide mouthwash, the patient was given 600mg of Ibuprofen. Anesthesia was achieved with a local infiltration of 2% Lidocaine with 1/100000 epinephrine and 4% Articane with epinephrine 1:200,000. A full thickness mucoperiosteal flap from the distal buccal line angle of #11 to the mesial buccal line angle of #16 was elevated with the crestal incision and vertical incision. Sites #12 and #13, however, were prepared for placement of 3.7 mm diameter x 13 mm length and 3.7 mm diameter x 11 mm length, internally hexed dental implants, respectfully (Fig 1).
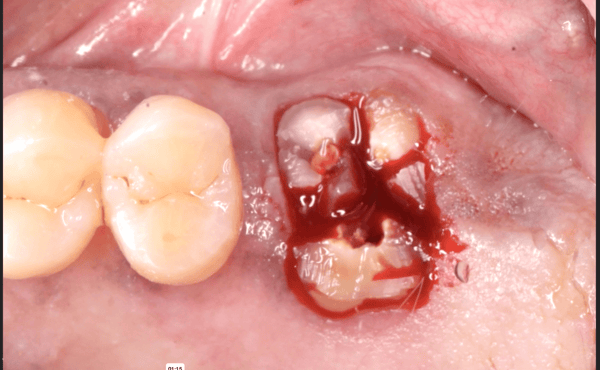
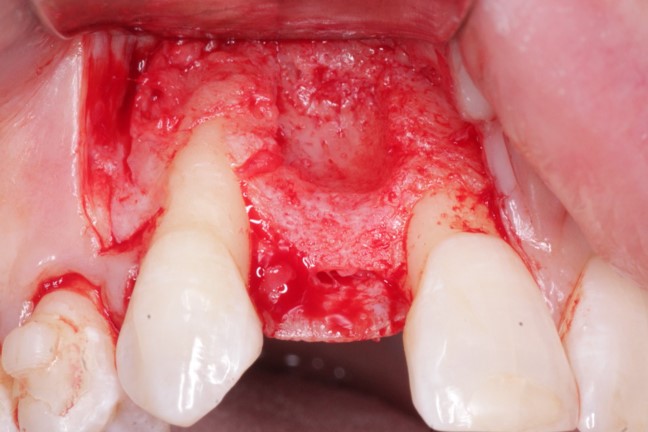
Lateral window approach to the sinus was prepared with a Piezo-electric surgical hoe to gain access through a circular window (Fig 2). The Schneiderian membrane was carefully elevated with Piezo-electric instrumentation as well as hand curettes. Two cc of SynOss„ Putty from Collagen Matrix Dental (Fig 3) was placed dry into the window and slightly compressed with a large surface bone condensing instrument.
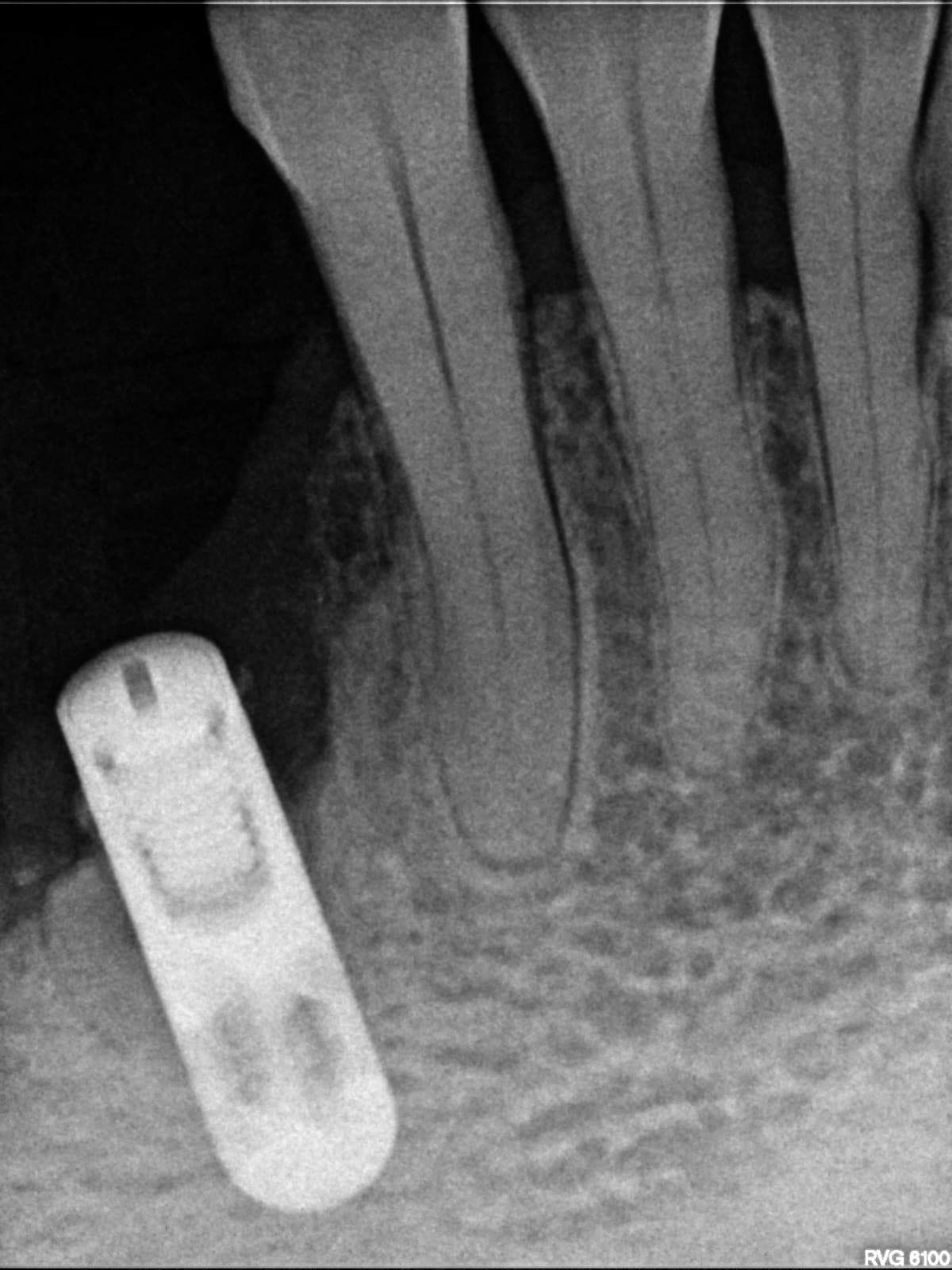
SynOss„ Putty molds and conforms upon hydration with blood and fluid to fill the defect site (Fig 4). A 30 x 40 mm porcine collagen membrane, MatrixDerm® Regenerative Collagen Membrane also by Collagen Matrix Dental, was hydrated in sterile saline, trimmed and placed over the lateral window (Fig 5). Primary closure was then obtained with 4-0 vicryl sutures in a continuous interlocking fashion and vertical incisions with interrupted sutures (Fig 6). Immediate post-operative radiographic image demonstrated placement of the dental implants along with placement of opaque well confined SynOss„ Putty grafting material (Fig 7). It is important to note that SynOss„ Putty can be visualized radiographically.
Post-Operative/Re-entry Surgical Procedure #2
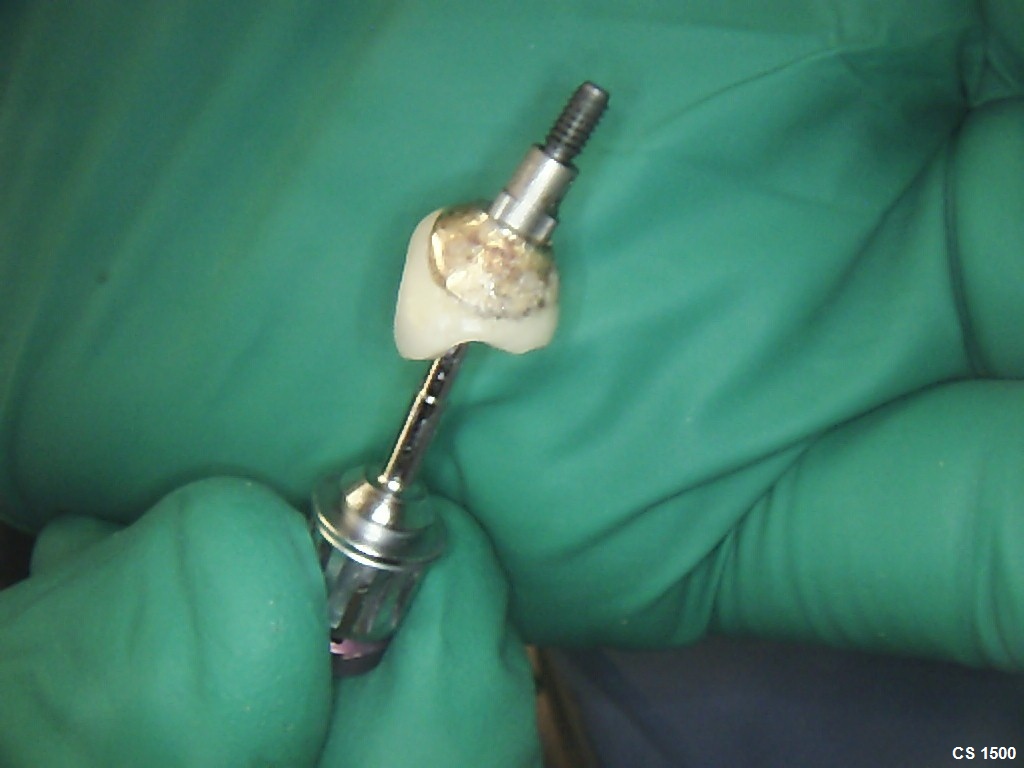
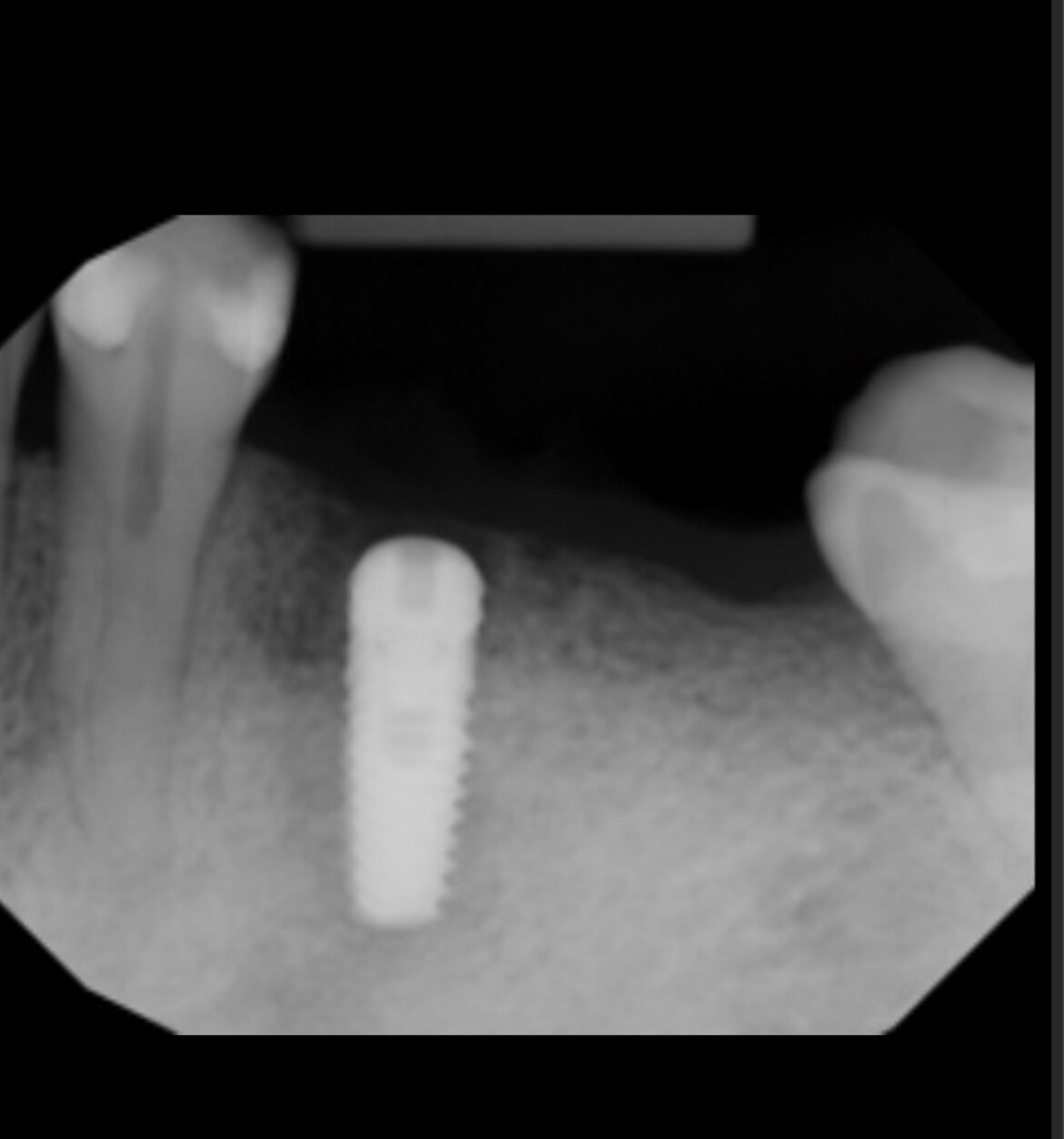
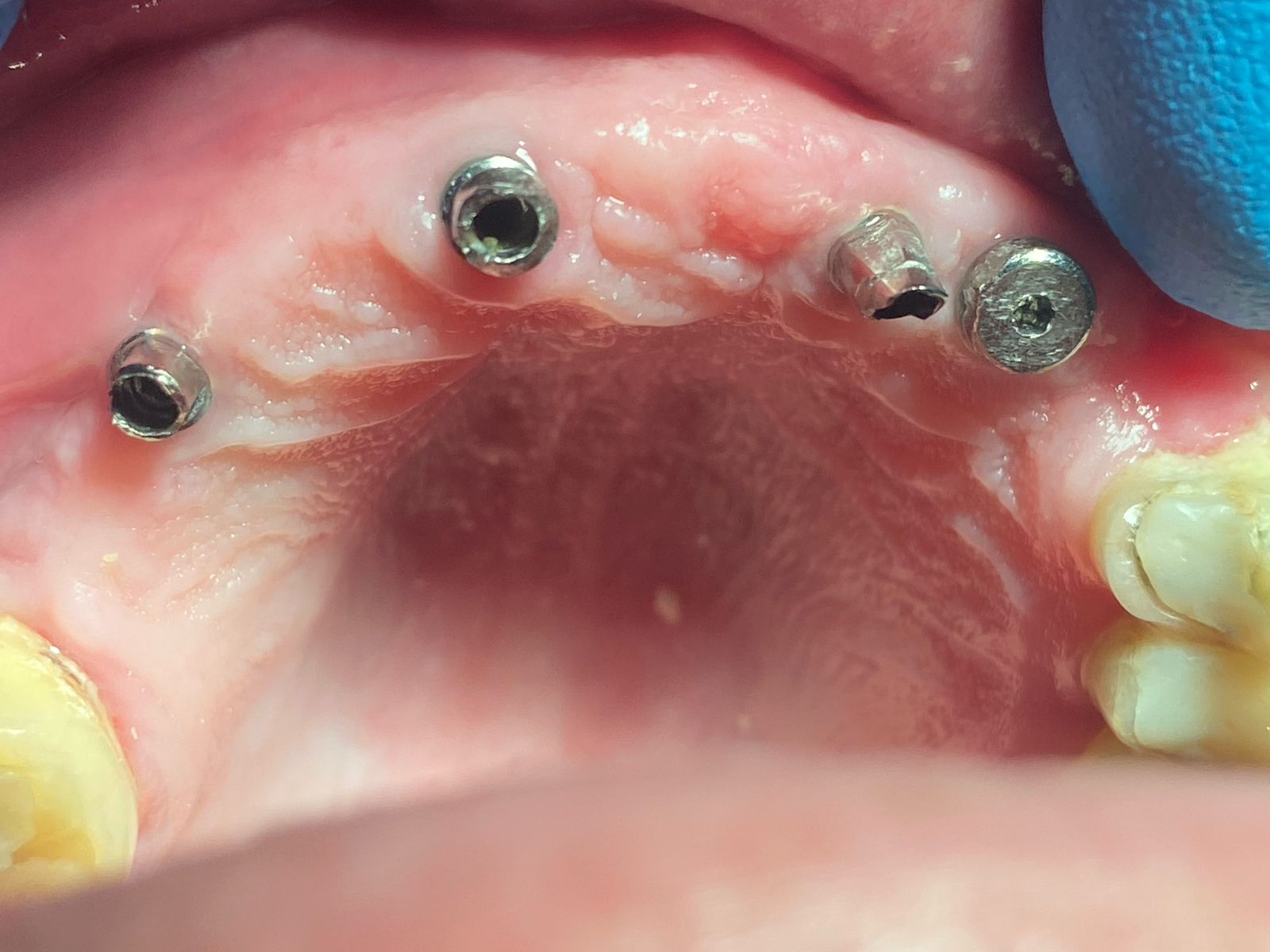
After completion of the first surgery, the patient was placed on 50 mg Amoxicillin three times daily for seven days and 600mg Ibuprofen for pain. Sutures were removed in 14 days and healing was unremarkable. Approximately 20 weeks later a second stage surgery was performed to expose osseo-integrated fixtures #12 and #13 for placement of healing abutments and to place dental implants in the #14 and #15 sites (Fig 8).
A mucoperiosteal flap was elevated as previously described. New bone had sufficiently filled the defect site to enable a 3.7 mm diameter x 13 mm length and 3.7 mm diameter x 10 mm length internally hexed dental implant to be placed into the #14 and #15 sites respectively and healing abutments were placed onto implants #12 and #13 (Fig 8). Implant osteotomies were performed for #14 and #15 with a hand piece at 800 rpm and primary fixation of the implants was obtained. The surgical site was closed with 4-0 vicryl suture in a continuous interrupted manner. Radiographic image showed healing abutments on sites #12 and #13 and dental implants #14 and #15 in grafted site with transfer copings attached (Fig 9). Sutures will be removed in approximately 2 weeks and second stage surgery is scheduled in 16 weeks for #14 and #15 from the time of this publication.
Conclusion
SynOss Putty and the MatrixDerm Collagen Membrane supported new bone formation in a larger sinus lift procedure to enable 2 dental implants to be placed approximately 20 weeks post implantation. Primary fixation was achieved.